

#Box and whisker plot skewed right how to
How to Interpret a Box Plotīefore we see how to create a box plot (also called a box and whisker chart), let us first learn to understand and interpret a box plot. In this way, box plots also help us find outliers and can tell if the data is symmetric or skewed.īox plots are especially helpful when you want to compare different sample distributions, and since it provides a 5-point summary of the entire dataset, it is really useful when the datasets you are studying are very large. They can be quite helpful when you want to see how the data is distributed and the range to which the data extends.
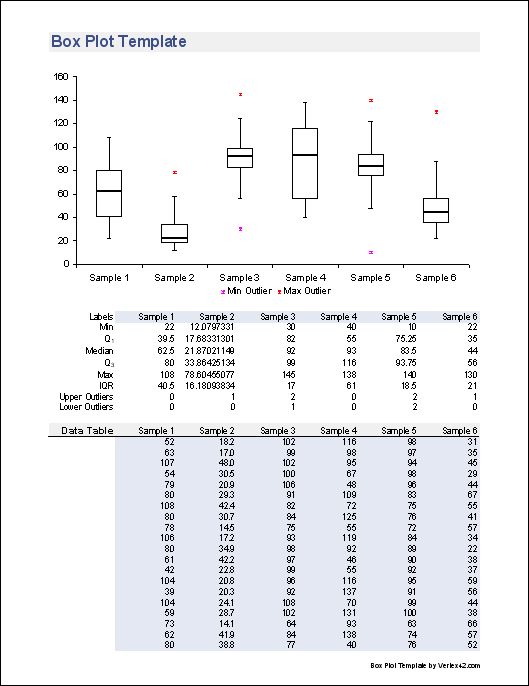
Why Use a Box Plot?Ī box plot is a great way to visually summarize your data using 5 descriptive indicators.
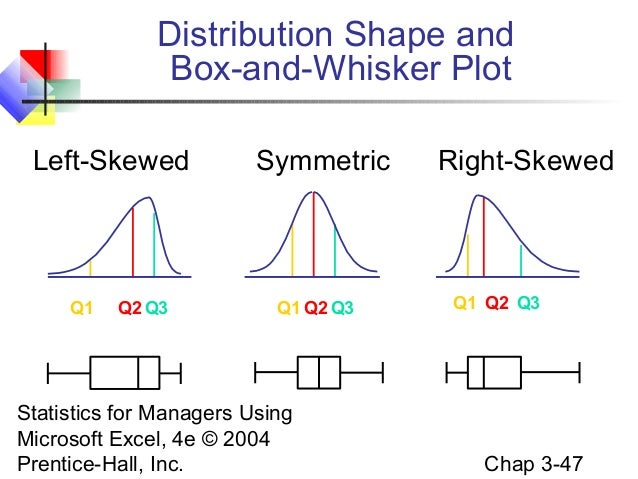
The width of the box basically marks the most concentrated area of the data distribution.Ī box plot can also contain ‘whiskers’ which are simply lines that depict the minimum and maximum values that are outside the first and third quartiles. The main ‘box’ of the box plot is drawn between the first and third quartiles, with an additional line drawn to represent the second quartile, or the ‘median’. The box plot divides numerical data into ‘quartiles’ or four parts. An example of a Box Plot chart created in Excel


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
